Release 0.14.0 (current release)¶
New features since last release
Programs compiled with
qjitcan now be visualized withdraw_graph(), allowing for sequentially analyzing impacts of compilation passes on structured and dynamic programs. (#2213) (#2214) (#2218) (#2229) (#2231) (#2234) (#2243) (#2246) (#2260) (#2285) (#2287) (#2298) (#2290) (#2340) (#2357) (#2309) (#2363) (#2380)Consider the following circuit:
import pennylane as qml import catalyst @qml.qjit(autograph=True) @catalyst.passes.cancel_inverses @catalyst.passes.merge_rotations @qml.qnode(qml.device("null.qubit", wires=3)) def circuit(x, y): qml.X(0) qml.Y(1) qml.H(x) qml.GlobalPhase(1.0) for i in range(3): qml.S(0) qml.RX(0.1, wires=1) qml.RX(0.2, wires=1) if i == 3: qml.T(0) else: qml.H(0) qml.H(0) qml.H(x) return qml.expval(qml.Z(y))
The circuit structure (
forloop and conditional branches) along with the dynamicism (variablesxandy) can be succinctly represented withdraw_graph().>>> x, y = 1, 0 >>> fig, ax = catalyst.draw_graph(circuit)(x, y) >>> fig.savefig('path_to_file.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches="tight")
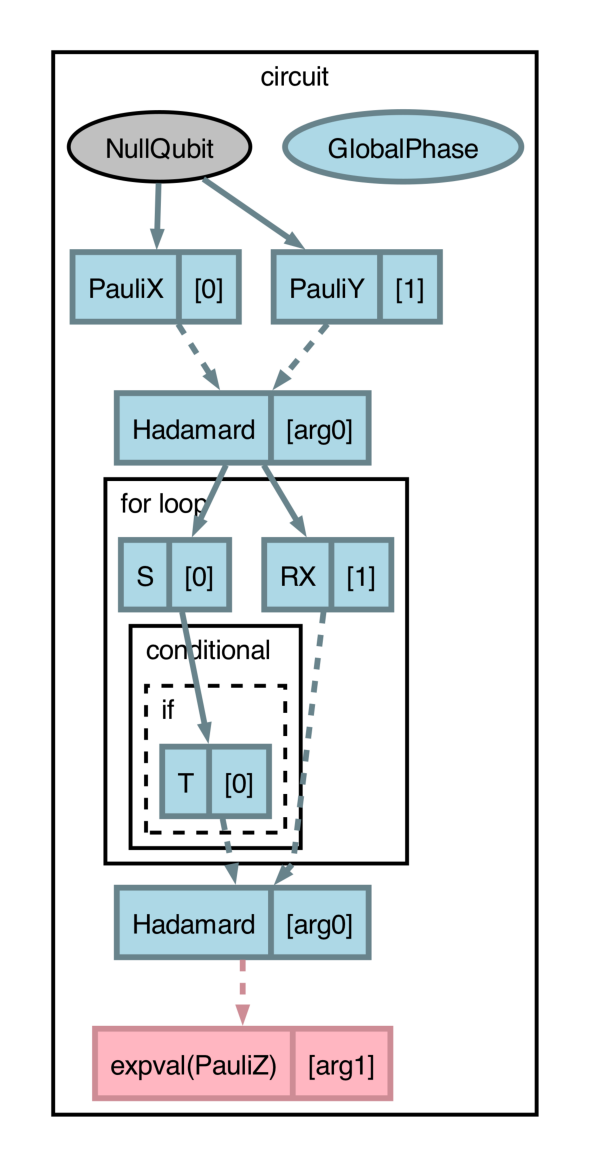
The output of
draw_graph()is amatplotlib.figure.Figure, allowing for natural manipulations like increasing resolution, size, etc.By default, all compilation passes specified will be applied and visualized. However,
draw_graph()can be used with thelevelargument to inspect compilation pass impacts, where thelevelvalue denotes the cumulative set of applied compilation transforms (in the order they appear) to be applied and visualized. Withlevel=1, drawing the above circuit will apply themerge_rotationtransform only:>>> fig, ax = catalyst.draw_graph(circuit, level=1)(x, y) >>> fig.savefig('path_to_file.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches="tight")
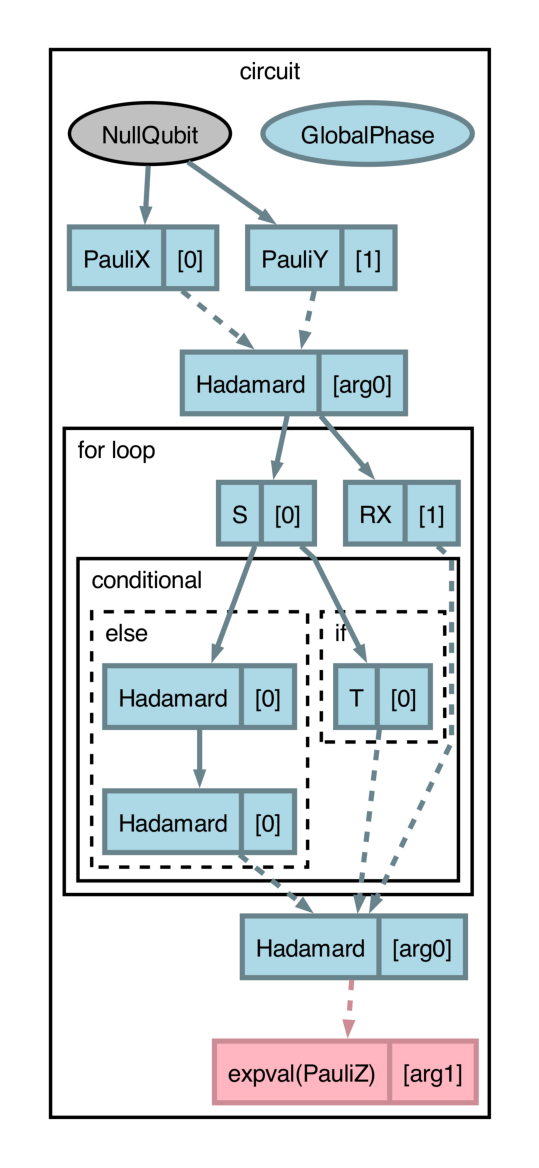
The
draw_graph()function visualizes aqjit-compiled QNode in a similar manner as view-op-graph does in MLIR, which leverages Graphviz to show data-flow in the compiled IR. As such, use ofdraw_graph()requires installation of Graphviz and the pydot software package. Please consult the links provided for installation instructions. Additionally, it is recommended to usedraw_graph()with PennyLane’s program capture enabled (seeqml.capture.enable).The Ross-Sellinger Gridsynth algorithm for discretizing
RZandPhaseShiftgates has been added to Catalyst withgridsynth(), allowing for Clifford+T workloads to benefit more from just-in-time compilation withqjit. (#2140) (#2166) (#2292)The
gridsynth()compilation pass discretizesRZandPhaseShiftgates to either the Clifford+T basis or to the Pauli-product-rotation (PPR) basis, complimenting existing transforms likepennylane.transforms.clifford_t_decomposition()and Pauli-based-computation compilation passes. This pass is also callable from the PennyLane frontend viapennylane.transforms.gridsynth().A new statevector simulator called
lightning.amdgpuhas been added for optimized performance on AMD GPUs, and is compatible with Catalyst. (#2283)The
lightning.amdgpudevice is a specific instantiation of thelightning.kokkosbackend, supporting the same features and operations aslightning.kokkos, with pre-compiled wheels forlightning.amdgpuavailable on PyPI for easy installation to use on MI300 series AMD GPUs.This device can be used within
qjit‘d workflows exactly as other devices compatible with Catalyst:@qml.qjit @qml.qnode(qml.device('lightning.amdgpu', wires=2)) def circuit(): qml.Hadamard(0) return qml.state()
>>> circuit() [0.70710678+0.j 0. +0.j 0.70710678+0.j 0. +0.j]
See the Lightning-AMDGPU documentation for more details and installation instructions.
A new control-flow operation has been added called
catalyst.switch(), which is aqjit-compatible index-switch style control flow decorator. Switches allow for more efficient, non-recursive lowering of distinct cases and can simplify control flow among multiple branches. (#2171)from catalyst import qjit, switch @qjit @qml.qnode(qml.device("lightning.qubit", wires=1)) def my_circuit(i, theta): @switch(i) # initialize a switch on variable i def my_switch(angle): # this is the default branch (required) qml.RX(angle, wires=0) @my_switch.branch(1) # create a branch with case i = 1 def my_branch(angle): qml.RY(angle, wires=0) @my_switch.branch(4) # create a branch with case i = 4 def my_branch_4(angle): qml.H(0) my_switch(theta) # must invoke the switch return qml.probs()
Catalyst can now compile circuits that are directly expressed in terms of Pauli product rotation (PPR) and Pauli product measurement (PPM) operations:
PauliRotandpauli_measure(), respectively. This is only supported with PennyLane program capture enabled (pennylane.capture.enable()). This support enables research and development spurred from A Game of Surface Codes (arXiv1808.02892). (#2145) (#2233) (#2284) (#2296) (#2336) (#2360)PauliRotandpauli_measure()can be manipulated with Catalyst’s existing passes for PPR-PPM compilation only when PennyLane program capture is enabled. This includespennylane.transforms.to_ppr(),pennylane.transforms.commute_ppr(),pennylane.transforms.merge_ppr_ppm(),pennylane.transforms.ppr_to_ppm(),pennylane.transforms.reduce_t_depth(),pennylane.transforms.decompose_arbitrary_ppr()andpennylane.transforms.ppm_compilation(). Note that these transforms must be called from the PennyLane frontend, not fromcatalyst.passes.import pennylane as qml import jax.numpy as jnp import catalyst qml.capture.enable() pipelines=[('pip', ["quantum-compilation-stage"])] @qml.qjit(pipelines=pipelines, target="mlir") @qml.transforms.ppm_compilation @qml.qnode(qml.device("null.qubit", wires=4)) def circuit(): # equivalent to a Hadamard gate qml.PauliRot(jnp.pi / 2, pauli_word="Z", wires=0) qml.PauliRot(jnp.pi / 2, pauli_word="X", wires=0) qml.PauliRot(jnp.pi / 2, pauli_word="Z", wires=0) # equivalent to a CNOT gate qml.PauliRot(jnp.pi / 2, pauli_word="ZX", wires=[0, 1]) qml.PauliRot(-jnp.pi / 2, pauli_word="Z", wires=[0]) qml.PauliRot(-jnp.pi / 2, pauli_word="X", wires=[1]) # equivalent to a T gate qml.PauliRot(jnp.pi / 4, pauli_word="Z", wires=0) ppm = qml.pauli_measure(pauli_word="ZXY", wires=[1, 2, 0]) return
>>> print(circuit.mlir_opt) ... %3 = qec.fabricate magic : !quantum.bit %mres, %out_qubits:2 = qec.ppm ["X", "Z"] %1, %3 : i1, !quantum.bit, !quantum.bit %mres_0, %out_qubits_1 = qec.select.ppm(%mres, ["Y"], ["X"]) %out_qubits#1 : i1, !quantum.bit %4 = qec.ppr ["X"](2) %out_qubits#0 cond(%mres_0) : !quantum.bit quantum.dealloc_qb %out_qubits_1 : !quantum.bit %5 = quantum.extract %0[ 2] : !quantum.reg -> !quantum.bit %mres_2, %out_qubits_3:3 = qec.ppm ["Z", "Y", "X"] %4, %2, %5 : i1, !quantum.bit, !quantum.bit, !quantum.bit ...
A new transform called
decompose_arbitrary_ppr()pass has been added, which decomposes abitrary-angle Pauli-product rotations (PPRs) as outlined in Figure 13(d) from arXiv:2211.15465. (#2304) (#2354)An arbitrary-angle PPR is defined as a PPR whose angle of rotation is not \(\tfrac{\pi}{2}\), \(\tfrac{\pi}{4}\), or \(\tfrac{\pi}{8}\). The
decompose_arbitrary_ppr()compilation pass will decompose an arbitrary-angle PPR into a collection of non-arbitrary PPRs, Pauli-product measurements (PPMs), and a single-qubit arbitrary PPR in theZbasis.For compatibility with
pennylane.specs(), it is recommended to use this transform with PennyLane program capture enabled and by calling it from the PennyLane frontend (pennylane.transforms.decompose_arbitrary_ppr()), not fromcatalyst.passes.import pennylane as qml qml.capture.enable() @qml.qjit(target="mlir") @qml.transforms.decompose_arbitrary_ppr @qml.transforms.to_ppr @qml.qnode(qml.device("null.qubit", wires=3)) def circuit(): qml.PauliRot(0.1, pauli_word="XY", wires=[0, 1]) return
>>> print(qml.specs(circuit, level=3)()) Device: null.qubit Device wires: 3 Shots: Shots(total=None) Level: 3 Resource specifications: Total wire allocations: 4 Total gates: 6 Circuit depth: Not computed Gate types: qec.prepare: 1 PPM: 2 PPR-pi/2: 2 PPR-Phi: 1 Measurements: No measurements.
Improvements 🛠
An informative error is now raised if a transform is applied inside of a
qjit‘d QNode when PennyLane’s program capture is enabled. (#2256)@qml.qjit @qml.qnode(qml.device('lightning.qubit', wires=1)) @qml.transforms.cancel_inverses def c(): qml.X(0) qml.X(0) return qml.probs()
>>> c() NotImplementedError: transforms cannot currently be applied inside a QNode.
qml.PCPhasecan now beqjit-compiled and executed with PennyLane’s program capture enabled. (#2226)The new graph-based decomposition framework (enabled with
pennylane.decomposition.enable_graph()) has Autograph feature parity with PennyLane when PennyLane’s program capture is enabled. When compiling withqml.qjit(autograph=True), the decomposition rules returned by the graph-based framework are now correctly compiled using Autograph. This ensures compatibility and deeper optimization for dynamically generated decomposition rules. (#2161)The decomposition of
qml.MultiRZoperations with an arbitrary number of wires is now supported at the MLIR level with graph-based decompositions enabled and PennyLane’s program capture enabled. (#2160)Catalyst can now use the new
pass_nameproperty of pennylane transform objects. Passes can now be created usingqml.transform(pass_name=pass_name)instead ofPassPipelineWrapper. This allows for better integration of Catalyst transforms with the PennyLane frontend. (#2149Compilation passes registered in PennyLane via
@qml.transformcan now take in optional keyword arguments when used withqjit()and when PennyLane’s program capture is enabled. (#2154)Pytree inputs can now be used when PennyLane’s program capture is enabled. (#2165)
The
ppr-to-mbqcpass now supports loweringqec.ppr.arbitraryoperations (Pauli Product Rotations with arbitrary angles) to MBQC-style gate sequences. The lowering follows the same pattern as fixed-angle PPR operations: conjugation gates to map Paulis to the Z-basis, a CNOT ladder to accumulate parity, an RZ gate with angle2θ(whereθis the PPR angle), and reverse operations to restore the original basis. (#2373)qml.gradandqml.jacobiancan now be used withqjitwhen PennyLane’s program capture is enabled. (#2078)A new
"changed"option has been added to thekeep_intermediateparameter ofqjit(). This option saves intermediate IR files after each pass, but only when the IR is actually modified by the pass. Additionally, intermediate IR files are now organized into subdirectories for each compilation stage when usingkeep_intermediate="changed"orkeep_intermediate="pass". These changes culminate in better IR file management. (#2186)Resource tracking with
pennylane.specs()now includesqml.StatePrepoperations and accounts for dynamic wire allocation (pennylane.allocate()). (#2230) (#2203)When saving the IR that each compilation pass generates, the
apply-transform-sequencepass is now counted as a single pass instead of potentially many passes. (#1978)A new option called
use_namelochas been added toqjit()that embeds variable names from Python into the compiler IR, which can make it easier to read when debugging programs. (#2054)Dynamically allocated wires (
pennylane.allocate()) can now be passed into control flow blocks and subroutines. (#2130) (#2268)The
--adjoint-loweringpass can now handle Pauli-product rotation (PPR) operations. (#2227)Catalyst now supports Pauli product rotations (PPR) with arbitrary or dynamic angles in the QEC dialect. This will allow
pennylane.PauliRotwith arbitrary or dynamic angles (angles not known at compile time) to be lowered to the QEC dialect. This is implemented as a newqec.ppr.arbitraryoperation, which takes a Pauli-product and an arbitrary or dynamic angle as input. (#2232) (#2233)For example:
%const = arith.constant 0.124 : f64 %1:2 = qec.ppr.arbitrary ["X", "Z"](%const) %q1, %q2 : !quantum.bit, !quantum.bit %2:2 = qec.ppr.arbitrary ["X", "Z"](%const) %1#0, %1#1 cond(%c0) : !quantum.bit, !quantum.bit
Catalyst now features a unified compilation framework, which will enable users and developers to design and implement compilation passes in Python in addition to C++, acting on the same Catalyst IR. The Python interface relies on the
xDSL library <https://xdsl.dev/>to represent and manipulate programs (analogous to the MLIR library in C++). As a result, transformations can be quickly prototyped, easily debugged, and dynamically integrated into Catalyst without changes to the compiled Catalyst package. (#2199)This new module is available under the
catalyst.python_interfacenamespace, and will feature more user-friendly functionality for writingqjit-compatible compilation passes in upcoming releases.This functionality was originally developed as part of the PennyLane package, and has been migrated here. For earlier development notes to the feature, please refer to the PennyLane release notes.
Here is a list of what’s included with this change:
Added the
PauliRotOp,PCPhaseOp, andPPRotationArbitraryOpoperations to the xDSL quantum dialect. (#2307) (#8621)An xDSL
Universecontaining all custom xDSL dialects and passes has been registered as an entry point, allowing usage of PennyLane’s dialects and passes with xDSL’s command-line tools. (#2208)A new
catalyst.python_interface.inspection.mlir_specsfunction has been added to facilitate PennyLane’s new pass-by-passpennylane.specs()feature withqjit. This function returns information gathered by parsing the xDSL-generated MLIR from a given QJIT object, such as gate counts, measurements, or qubit allocations. (#2238) (#2303) (#2315)Added an experimental
outline_state_evolution_passxDSL pass tocatalyst.python_interface.transforms, which moves all quantum gate operations to a private callable. (#8367)A new experimental
split_non_commuting_passcompiler pass has been added tocatalyst.python_interface.transforms. This pass splits quantum functions that measure observables on the same wires into multiple function executions, where each execution measures observables on different wires (using the"wires"grouping strategy). The original function is replaced with calls to these generated functions, and the results are combined appropriately. (#8531)Users can now apply xDSL passes without the need to pass the
pass_pluginsargument to theqjitdecorator. (#8572) (#8573) (#2169) (#2183)The
catalyst.python_interface.transforms.convert_to_mbqc_formalism_pass()now supportsIndexSwitchOpin the IR and ignores regions that have no body. (#8632)The
convert_to_mbqc_formalismcompilation pass now outlines the operations to represent a gate in the MBQC formalism into subroutines in order to reduce the IR size for large programs. (#8619)The
catalyst.python_interface.Compiler.run()method now accepts a string as input, which is parsed and transformed with xDSL. (#8587)An
is_xdsl_passfunction has been added to thecatalyst.python_interface.pass_apimodule. This function checks if a pass name corresponds to an xDSL implemented pass. (#8572)A new
catalyst.python_interface.utilssubmodule has been added, containing general-purpose utilities for working with xDSL. This includes a function that extracts the concrete value of scalar, constant SSA values. (#8514)The
catalyst.python_interface.visualizationmodule has been renamed tocatalyst.python_interface.inspection, and various utility functions within this module have been streamlined. (#2237)The experimental xDSL
measurements_from_samples_pass()pass has been updated to supportshotsdefined by anarith.constantoperation. (#8460)Removed the
catalyst.python_interface.dialects.transformmodule in favor of using thexdsl.dialects.transformmodule directly. (#2261)Added a “Unified Compiler Cookbook” RST file, along with tutorials, to
catalyst.python_interface.doc, which provides a quickstart guide for getting started with xDSL and its integration with PennyLane and Catalyst. (#8571)xDSL passes are now automatically detected when using the
qjitdecorator. This removes the need to pass thepass_pluginsargument to theqjitdecorator. (#2169) (#2183)The
mlir_optproperty now correctly handles xDSL passes by automatically detecting when the Python compiler is being used and routing through it appropriately. (#2190)A new experimental
parity_synth_passcompiler pass has been added tocatalyst.python_interface.transforms. This pass groupsCNOTandRZoperators into phase polynomials and re-synthesizes them intoCNOTandRZoperators again. (#2294)The
catalyst.python_interface.pass_api.PassDispatchernow has a more lightweight implementation. (#2324)The global xDSL pass registry is now explicitly refreshed before compiling workflows decorated with
catalyst.qjit(). (#2322)
Breaking changes 💔
The standard Catalyst pipelines have been restructured, such that default and user QNode passes are run together in the first pipeline. For this purpose, the old
quantum-compilation-pipelineandenforce-runtime-invariants-pipelinehave been merged into a singlequantum-compilation-pipeline, while a newgradient-lowering-pipelinehas been split out from the oldquantum-compilation-pipeline. (#2186)The
pipelineand"passes"postfixes in the compilation stage names have been changed tostagefor clarity. (#2230)The JAX version used by Catalyst has been updated to 0.7.0. (#2131)
(Compiler integrators only) The versions of LLVM/Enzyme/stablehlo used by Catalyst have been updated. (#2122) (#2174) (#2175) (#2181)
The LLVM version has been updated to commit 113f01a.
The stablehlo version has been updated to commit 0a4440a.
The Enzyme version has been updated to v0.0.203.
The
remove-chained-self-inversepass has been renamed tocancel-inversesto better conform with the name of the corresponding transform in PennyLane. (#2201)The
to-pprpass now automatically runs canonicalization patterns after converting quantum operations to Pauli Product Rotation (PPR) form. This removes identity Pauli rotations (e.g.,["I", "I", "I"]) automatically, simplifying the resulting IR. (#2367)
Deprecations 👋
No deprecations have been made in this release.
Bug fixes 🐛
Fixed a bug in the
catalyst.passes.merge_ppr_ppm()that was causing an iteration out-of-bound error. (#2359)Updated the type support for callbacks allowing for the use of unsigned integers. (#2330)
Fixed a bug in the
gradient.value_and_gradverifier that incorrectly validated gradient result types by matching from the tail of callee arguments, ignoringdiffArgIndices. This caused false verification errors when differentiating a subset of arguments with different types. (#2349)Fixed a bug in the
catalyst.python_interface.pass_api.TranformInterpreterPasspass that prevented pass options from being used correctly. (#2289)The experimental xDSL
diagonalize_measurements()pass has been updated to fix a bug that included the wrong SSA value for final qubit insertion and deallocation at the end of the circuit. A clear error is now also raised when there are observables with overlapping wires. (#8383)Fixed a bug in the constructor of the xDSL Quantum dialect’s
QubitUnitaryOpthat prevented an instance from being constructed. (#8456)Fixed a bug where the
qec.pprop attributerotation_kindwas not correctly constrained to be one of±1,±2,±4, or±8. Also, for the identity Pauli product, therotation_kindwas correctly set to1, instead of0. (#2344)Running the Catalyst compiler from the command line no longer misses the
detensorize-function-boundaryandsymbol-dcepasses. (#2266)Fixed an issue where a heap-to-stack allocation conversion pass was causing SIGSEGV issues during program execution at runtime. (#2172)
Fixed an issue with capturing unutilized abstracted adjoint and controlled rules by the graph in the new decomposition framework. (#2160)
Fixed the translation of PennyLane control flow (
qml.for_loop) to Catalyst control flow for edge cases where theconstswere being reordered. (#2128) (#2133)Fixed the translation of
QubitUnitaryandGlobalPhaseoperations to Catalyst when they are modified byadjointorctrl. (##2158)Fixed an issue with the translation of a workflow with different transforms applied to different QNodes, which was causing transforms to act beyond the code they are intended to be applied to. (#2167)
Fixed canonicalization of redundant
quantum.insertandquantum.extractpairs. When extracting a qubit immediately after inserting it at the same index, the operations can be cancelled out while properly updating remaining uses of the register. (#2162)For an example:
// Before canonicalization %1 = quantum.insert %0[%idx], %qubit1 : !quantum.reg, !quantum.bit %2 = quantum.extract %1[%idx] : !quantum.reg -> !quantum.bit ... %3 = quantum.insert %1[%i0], %qubit2 : !quantum.reg, !quantum.bit %4 = quantum.extract %1[%i1] : !quantum.reg -> !quantum.bit // ... use %1 // ... use %4 // After canonicalization // %2 directly uses %qubit1 // %3 and %4 updated to use %0 instead of %1 %3 = quantum.insert %0[%i0], %qubit2 : !quantum.reg, !quantum.bit %4 = quantum.extract %0[%i1] : !quantum.reg -> !quantum.bit // ... use %qubit1 // ... use %4
Fixed an issue with
commute_ppr()andmerge_ppr_ppm()where they were incorrectly moving operations. This also improves the compilation time by reducing the sort function by explicitly passing the operations that need to be sorted. (#2200)Fixed a bug that was causing compilation passes to not apply when using
mcm_method="one-shot". (#2198)Fixed a bug where
qml.StatePrepandqml.BasisStatemight be pushed after other gates, overwriting their effects. (#2239)Fixed a bug where
quantum.num_qubitsoperations were not properly removed during classical processing of gradient transforms. This fix enables automatic qubit management (i.e., creating a device and not providing thewiresargument) to be used with gradients. (#2262)Fixed a but with
commute_ppr()that was incorrectly modifying operands of PPRs that live in different blocks of MLIR. (#2267)The
--inline-nested-modulepass no longer renames external function declarations. This pass inlines the QNode MLIR modules into the global QJIT MLIR module. If a QNode module contains function declarations to external APIs, the names of these declarations must stay unchanged. This change enables quantum compilation passes to generate calls to external APIs. (#2244)Fixed a bug where Catalyst was incorrectly raising an error about a missing shots parameter on devices that support analytical execution. (#2281)
Fixed a bug where
qml.vjpandqml.jvpwere not working with Autograph. (#2345)Fixed incorrect detection of tracer wires in the frontend. Previously, NumPy integers would be detected as dynamic wires leading to unnecessary instructions in the program IR. (#2361)
Internal changes ⚙️
The jaxpr transform
pl_map_wireshas been removed along with its test. (#2220)DecompRuleInterpreternow solves the graph and adds decompositions rules in thecleanupmethod instead of during the first call tointerpret_measurement. (#2312)Updated references to
TransformProgramwith the newpennylane.CompilePipelineclass. (#2314)xDSL and xDSL-JAX are now dependencies of Catalyst. (#2282)
Python 3.14 is now officially supported. Added the forward capability with Python 3.14. (#2271)
The RTIO dialect is added to bypass the compilation flow from OpenAPL to ARTIQ’s LLVM IR. It is introduced to bridge the gap between the ion dialect and ARTIQ’s LLVM IR. The design philosophy of the RTIO dialect is primarily event-based. Every operation is asynchronous; sync behaviour occurs only via
rtio.syncorwait operandin event operation. And we now support the compiling from the ion dialect to the RTIO dilalect. (#2185) (#2204)Integration tests for
qml.specshave been updated to match the new output format introduced in PennyLane v0.44. (#2255)Resource tracking now writes out at device destruction time instead of qubit deallocation time. The written resources will be the total amount of resources collected throughout the lifetime of the execution. For executions that split work between multiple functions (e.g., with the
split-non-commutingpass), this ensures that resource tracking outputs the total resources used for all splits. (#2219)Replaced the deprecated
shape_dtype_to_ir_typefunction with theRankedTensorType.getmethod. (#2159)Updates to PennyLane’s use of a single transform primitive with a
transformkwarg. (#2177)The pytest tests are now run with
strict=Trueby default. (#2180)Refactored Catalyst’s pass registering so that it’s no longer necessary to manually add new passes at
registerAllCatalystPasses. (#1984)Split
from_plxpr.pyinto two files. (#2142)Re-worked
DataViewto avoid an axis of size0possibly triggering a segfault via an underflow error, as discovered in this comment. (#1621)Decoupled the ION dialect from the quantum dialect to support the new RTIO compilation flow. The ion dialect now uses its own
!ion.qubittype instead of depending on!quantum.bit. Conversion between qubits of quantum and ion dialects is handled via unrealized conversion casts. (#2163)For an example, quantum qubits are converted to ion qubits as follows:
%qreg = quantum.alloc(1) : !quantum.reg %q0 = quantum.extract %qreg[0] : !quantum.reg -> !quantum.bit // Convert quantum.bit to ion.qubit %ion_qubit_0 = builtin.unrealized_conversion_cast %q0 : !quantum.bit to !ion.qubit // Use in ion dialect operations %pp = ion.parallelprotocol(%ion_qubit_0) : !ion.qubit { ^bb0(%arg1: !ion.qubit): // ... ion operations ... }
Added support for
ppr-to-ppmas an individual MLIR pass and Python binding for the qec dialect. (#2189)Added a canonicalization pattern for
qec.pprto remove any PPRs consisting only of identities. (#2192)Renamed the
annotate-functionpass toannotate-invalid-gradient-functionsand moved it to the gradient dialect and thelower-gradientscompilation stage. (#2241)Added support for PPRs and arbitrary-angle PPRs to the
merge_rotations()pass. This pass now merges PPRs with equivalent angles, and cancels PPRs with opposite angles, or angles that sum to identity when the angles are known. The pass also supports conditions on PPRs, merging when conditions are identical and not merging otherwise. (#2224) (#2245) (#2254) (#2258) (#2311)Refactored QEC tablegen files to separate QEC operations into a new
QECOp.tdfile (#2253Removed the
getRotationKindandsetRotationKindmethods from the QEC interfaceQECOpInterfaceto simplify the interface. (#2250)A new
PauliFramedialect has been added. This dialect includes a set of abstractions and operations for interacting with an external Pauli frame tracking library. (#2188)A new
to-pauli-framecompilation pass has been added, which applies the Pauli frame tracking protocols to a Clifford+T program. (#2269)Adding the measurement type into the MLIR assembly format for
qec.ppmandqec.select.ppm(#2347)Remove duplicate code for canonicalization and verification of Pauli Product Rotation operations. (#2313)
Documentation 📝
A note was made in the Sharp Bits page for the behaviour of
qml.transforms.decomposewhen graph-based decompositions are enabled withpennylane.decomposition.enable_graph(). It clarifies that non-deterministic graph solutions may lead to non-executable programs if intermediate gates are not executable by Catalyst. (#2377)Clarifications were made in the Sharp Bits page for the behaviour of
qml.allocatewhen used with Catalyst. In particular, returning any terminal measurement besidesqml.probswhenqml.allocateis used within aqjit‘d workflow is not supported. (#2317) (#2358)A typo in the code example for
ppr_to_ppm()has been corrected. (#2136)Fixed a rendering issue in
catalyst.qjitandcatalyst.CompileOptionsdocstrings. (#2156)Updated the MLIR Plugins documentation stating that plugins require adding passes via
--pass-pipeline. (#2168)Typos in the docstrings for
PPRotationArbitraryOpandPPRRotationOphave been corrected. (#2297)The
--save-ir-after-eachcommand line option documentation has been updated to explain thechangedvalue. (#2355)
Contributors ✍️
This release contains contributions from (in alphabetical order):
Ali Asadi, Joey Carter, Yushao Chen, Isaac De Vlugt, Sengthai Heng, David Ittah, Jeffrey Kam, Christina Lee, Joseph Lee, Mehrdad Malekmohammadi, River McCubbin, Lee J. O’Riordan, Mudit Pandey, Andrija Paurevic, Roberto Turrado, Paul Haochen Wang, David Wierichs, Jake Zaia, Hongsheng Zheng.